Electrocardiogram Specialist in Michigan
CardioQ – Heart & Wellness Center is a leading healthcare provider in Michigan that specializes in providing exceptional cardiac care services to patients. At the heart of its success lies a team of highly skilled and experienced Electrocardiogram specialist, who are committed to ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
ECG specialists at CardioQ are equipped with the latest technology and expertise in interpreting electrocardiograms, a test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. They work closely with patients to diagnose and manage a variety of cardiac conditions, including arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other abnormalities.
With a focus on patient-centered care, Electrocardiogram specialist at CardioQ are dedicated to providing individualized treatment plans that address the unique needs of each patient. They work collaboratively with other healthcare professionals to ensure that patients receive comprehensive and coordinated care throughout their treatment.
At CardioQ, patients can trust that they are receiving the highest level of care from a team of dedicated ECG specialists who are committed to helping them achieve optimal cardiovascular health.
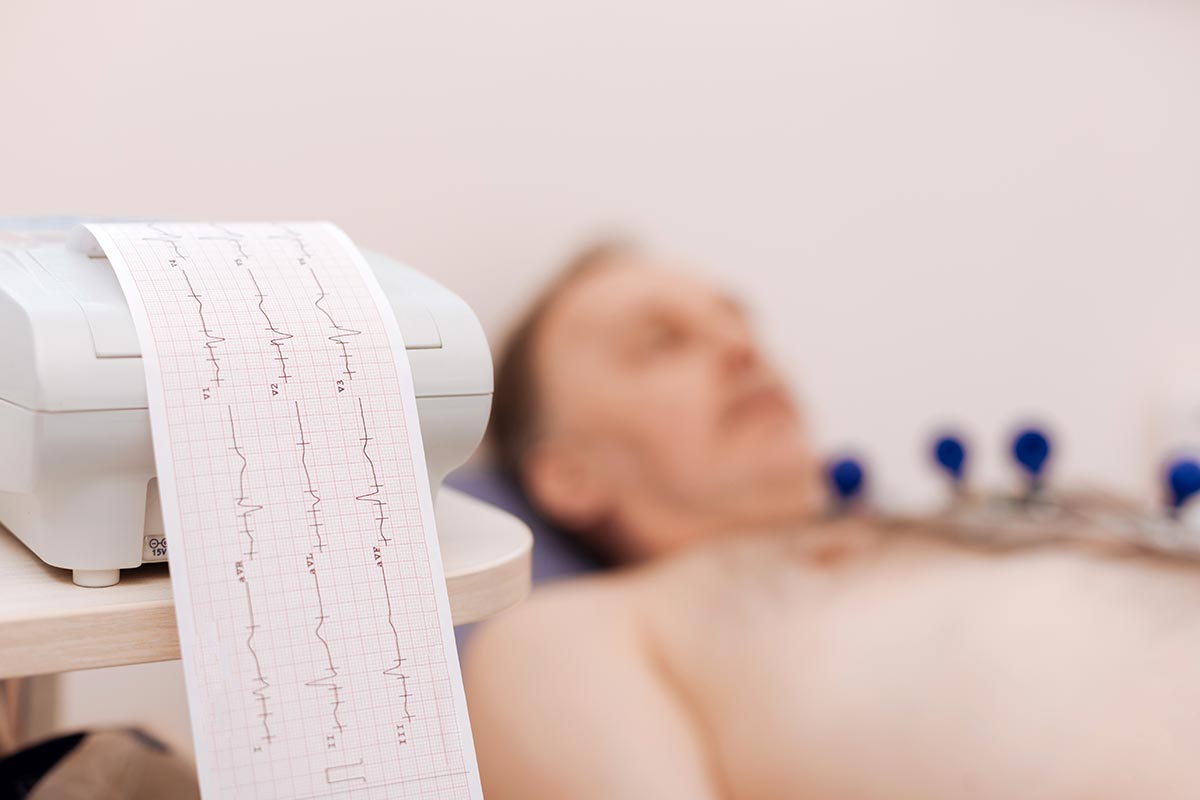
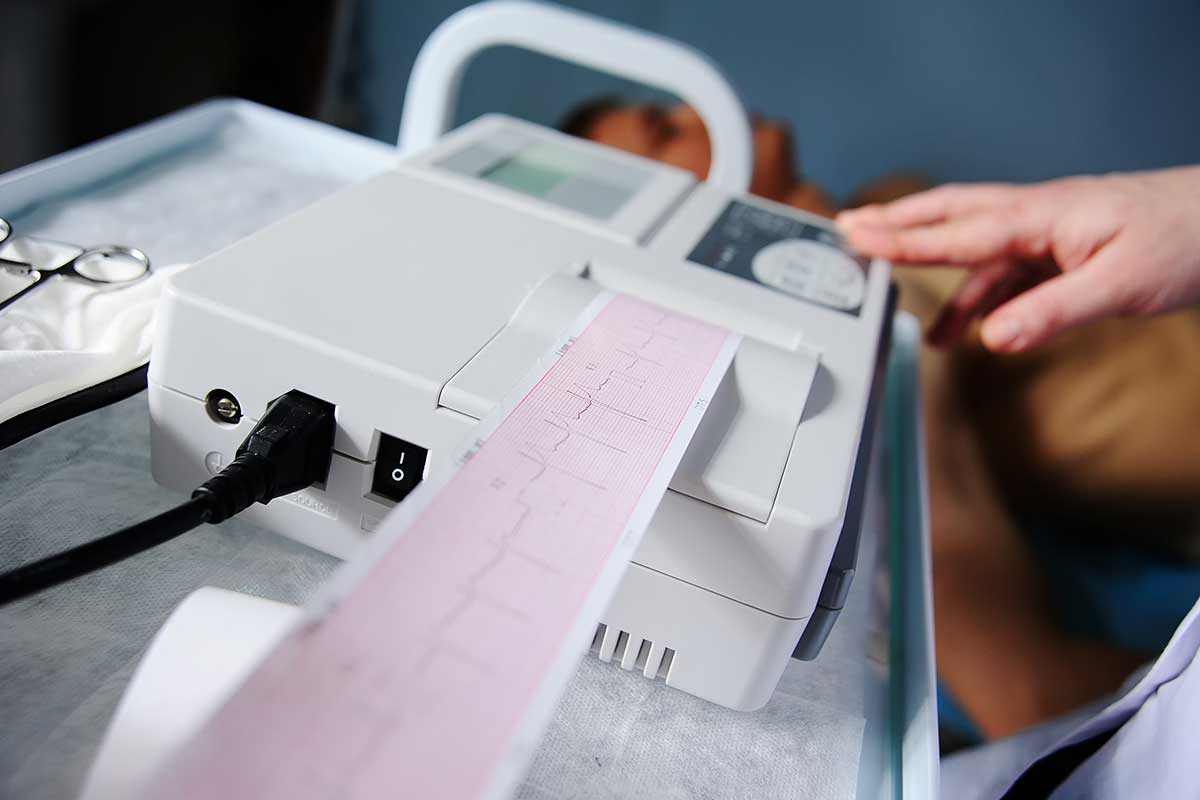
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
An electrocardiogram, also known as an ECG or EKG, is a diagnostic test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. It is a non-invasive and painless procedure that involves placing electrodes on the chest, arms, and legs to record the heart’s electrical impulses.
The ECG machine then produces a graph or tracing of these electrical impulses, which can help doctors detect a variety of heart problems, such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and abnormalities in heart structure or function. It can also help monitor the effectiveness of certain cardiac treatments, such as pacemakers or medications.
Overall, electrocardiograms are an important tool for diagnosing and managing a variety of cardiac conditions and are routinely used in both inpatient and outpatient settings.
Time it Takes
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a relatively quick and simple test that usually takes only a few minutes to complete. The exact duration of the test can vary depending on the specific protocol used by the healthcare provider or facility conducting the test, but most ECGs can be completed within 5-10 minutes.
During the ECG, the patient lies down on a bed or exam table while electrodes are placed on the chest, arms, and legs. The electrodes are connected to an ECG machine, which records the heart’s electrical activity. The patient needs to lie still and avoid talking or moving during the recording process to ensure accurate results.
Once the recording is complete, the electrodes are removed, and the results are analyzed by a healthcare provider or Electrocardiogram Specialist. In most cases, the patient can resume their normal activities immediately after the test.
Getting the Results
After an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) test, the results are typically interpreted by a healthcare provider or Electrocardiogram Specialist, such as a cardiologist. The ECG machine produces a graph or tracing of the heart’s electrical activity, which is then analyzed to identify any abnormalities or signs of cardiac conditions.
The results of an ECG may be classified as either normal or abnormal, depending on the findings. Normal results indicate that the heart is functioning properly, and there are no signs of cardiac problems or abnormalities. Abnormal results, on the other hand, may suggest the presence of a cardiac condition or abnormality, such as an arrhythmia, heart attack, or structural abnormality.
Overall, electrocardiogram results are an important tool for diagnosing and managing a variety of cardiac conditions, and they can provide valuable information to healthcare providers to ensure patients receive appropriate care.
Common questions
Your healthcare provider may recommend an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) for several reasons, including:
- To diagnose a heart condition: An ECG can help identify a variety of heart problems, such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and abnormalities in heart structure or function.
- To monitor heart health: If you have an existing heart condition or are taking medications that affect your heart, an ECG can help monitor your heart health and assess the effectiveness of your treatment.
- To screen for heart disease: An ECG may be recommended as part of a routine physical exam or health screening to check for signs of heart disease or risk factors.
- To evaluate chest pain or other symptoms: If you are experiencing chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, or other symptoms that may be related to your heart, an ECG can help evaluate the cause of your symptoms.
There are several types of electrocardiograms (ECGs or EKGs), each designed to provide different types of information about the heart. Some common types of ECGs include:
- Resting ECG: This is the most common type of ECG and involves recording the heart’s electrical activity while the patient is lying down and at rest.
- Exercise stress test: This type of ECG involves recording the heart’s electrical activity while the patient exercises on a treadmill or stationary bike. It can help identify abnormal heart rhythms or other cardiac problems that may only occur during exercise.
- Holter monitor: This is a portable ECG device that records the heart’s electrical activity continuously over a 24- to 48-hour period, allowing healthcare providers to evaluate the heart’s function during normal activities.
- Event monitor: This is a portable ECG device that records the heart’s electrical activity for short periods of time (usually up to a few minutes) in response to specific symptoms or events, such as palpitations or chest pain.
- Signal-averaged ECG: This is a specialized ECG that uses advanced algorithms to filter out extraneous electrical noise and provide a more detailed analysis of the heart’s electrical activity.
Overall, the type of ECG recommended will depend on the specific symptoms or concerns being evaluated, as well as the healthcare provider’s clinical judgment and expertise.
The test is performed by a specially trained healthcare provider called an echocardiogram specialist or echocardiographer. Here’s an overview of how an echocardiogram is typically performed:
- Preparation: Before the test, the echocardiogram specialist will explain the procedure and answer any questions you may have. You may be asked to change into a gown and lie down on an exam table.
- Electrodes: The echocardiogram specialist will attach small electrodes to your chest to monitor your heart’s electrical activity during the test.
- Gel: The specialist will apply a gel to your chest to help transmit the sound waves.
- Transducer: The specialist will then use a device called a transducer, which emits high-frequency sound waves, to capture images of your heart. The transducer is placed on different areas of your chest to obtain different views of the heart.
- Images: The sound waves bounce off the structures of the heart and are picked up by the transducer, which creates images of the heart on a computer screen. The echocardiogram specialist will adjust the transducer and take measurements to capture the necessary images of the heart.
- Completion: Once the images have been captured, the echocardiogram specialist will clean the gel off your chest and remove the electrodes. The entire test typically takes around 30-60 minutes to complete.
After the test, a healthcare provider or specialist will review the images to assess the heart’s structures and function and make a diagnosis if necessary. Echocardiograms are a safe and non-invasive way to evaluate heart health, and they can provide valuable information to help manage a variety of cardiac conditions.
Interpreting electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) results requires a trained healthcare provider, such as a cardiologist or electrophysiologist. The results of an ECG can provide information about the heart’s electrical activity, and can help diagnose a variety of heart conditions. Here are some common findings and what they may indicate:
- Normal sinus rhythm: If the ECG shows a normal sinus rhythm, it means that the heart’s electrical activity is normal and there are no signs of disease or abnormalities.
- Abnormal rhythm: The ECG may show an abnormal rhythm, such as atrial fibrillation, which can cause symptoms like palpitations, shortness of breath, or fatigue.
- ST-segment changes: The ECG may show ST-segment changes, which can be a sign of a heart attack or ischemia (reduced blood flow to the heart muscle).
- QT prolongation: The ECG may show a prolongation of the QT interval, which can be a sign of a genetic condition or medication side effect that increases the risk of a dangerous arrhythmia called torsades de pointes.
- Other abnormalities: The ECG may show other abnormalities, such as an enlarged heart or conduction abnormalities that can affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively.
It’s important to remember that interpreting ECG results requires a comprehensive evaluation by a trained healthcare provider who can take into account your medical history, symptoms, and other factors that may affect your heart health. Your provider will work with you to develop a treatment plan that meets your individual needs based on the results of the ECG and other diagnostic tests.
