Cardiac Pacemaker Specialist in Michigan
Cardiac pacemaker specialists are healthcare professionals who specialize in the management and maintenance of cardiac pacemakers, which are medical devices that regulate the heart’s rhythm.
In Michigan, CardioQ is one of the leading heart and healthcare provider that offers a range of cardiac services, including the expertise of cardiac pacemaker specialists. These specialists are trained and experienced in the implantation, programming, and troubleshooting of pacemakers, ensuring that patients receive the best possible care for their heart conditions.
In this intro, we will delve into the role of a cardiac pacemaker specialist at CardioQ and the importance of their work in supporting the health and wellbeing of patients with heart conditions in Michigan.
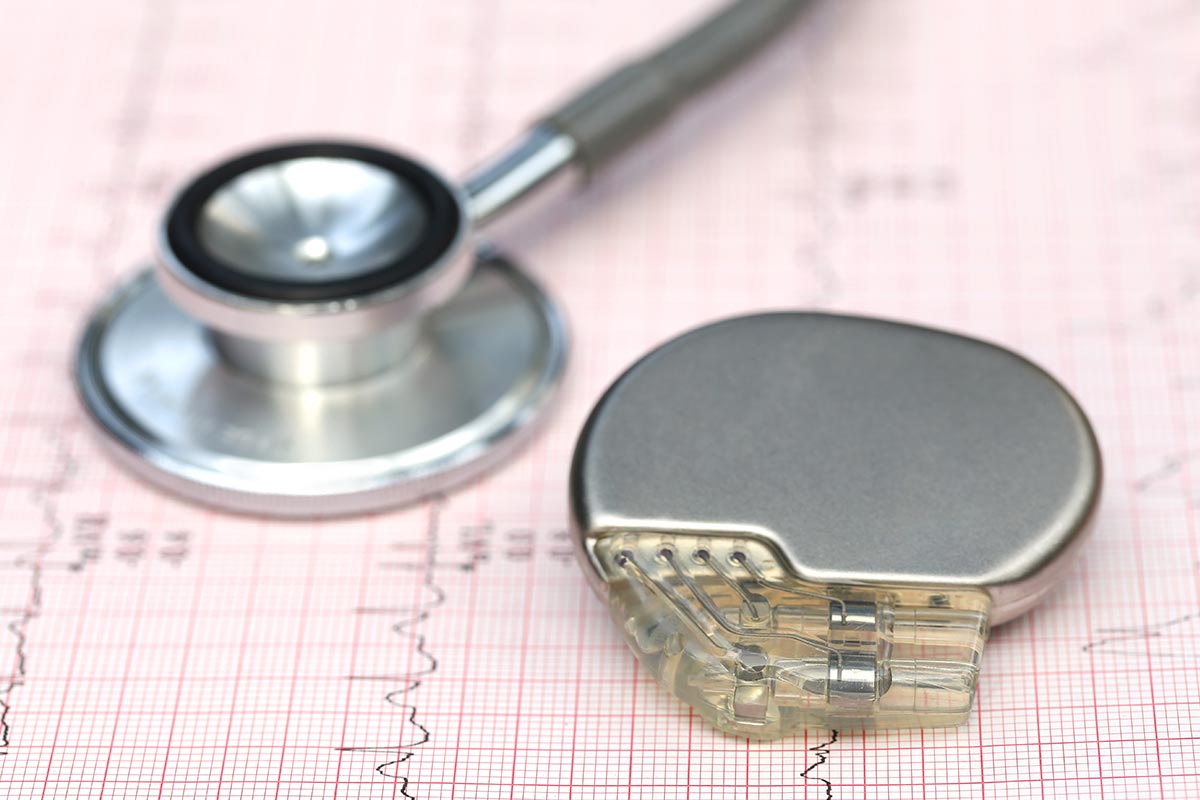
Cardiac Pacemaker
A pacemaker or cardiac pacemaker is a very small battery-operated device that generates electrical impulses to help your heart function normally.
Our Cardiac Pacemaker Specialist in Michigan at CardioQ are experts in precise pacemaker programming to keep your heartbeat in a normal range.
A pacemaker delivers mild electrical signals to your heart to help it beat at a normal rate and pump more effectively. When a pacemaker detects an abnormal heart rhythm, such as low heart rate, the device sends an electric pulse to your heart. The pulse stimulates your heart to beat faster, keeping its beat at a normal rate.
Our cardiologist uses pacemakers to sense and correct certain types of arrhythmias (abnormal heart rates or rhythms), most commonly these two types:
- Bradycardia: Heart rate that is too slow.
- Heart block: Electrical signals that are slowed or disrupted as they travel from the upper to the lower chambers of the heart.
Pacemaker Device
Our Cardiac Pacemaker Specialist in Michigan at CardioQ are experts in precise pacemaker programming to keep your heartbeat in a normal range. You can have your device adjusted in our clinic, or we can monitor you remotely to manage your pacemaker
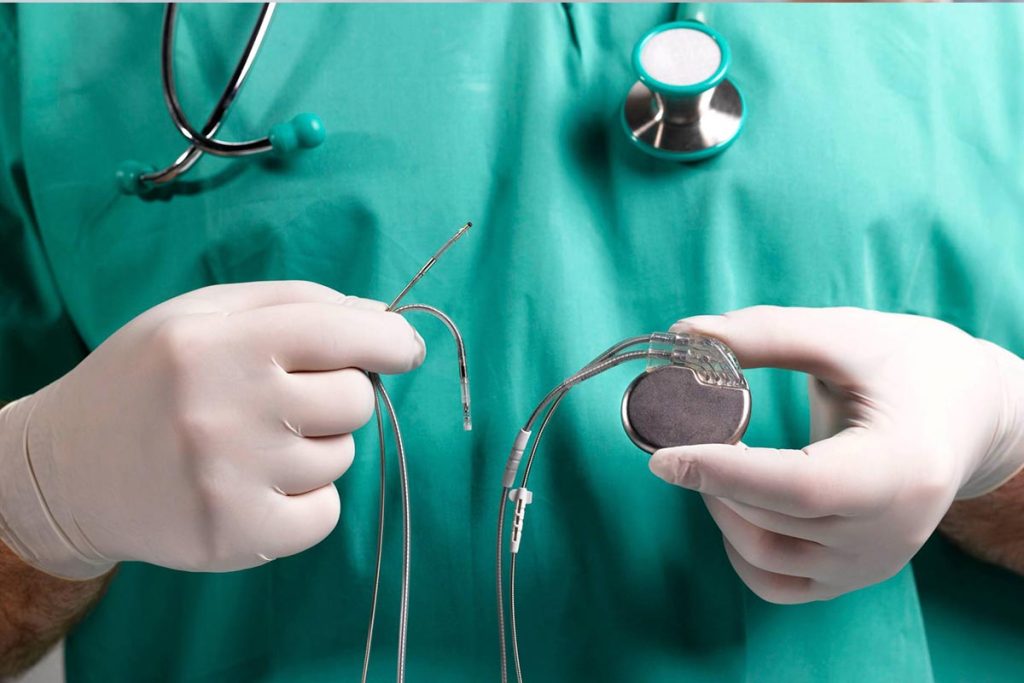
Components
The pacemaker device has four main parts:
- A computerized pulse generator to produce electrical signals to regulate your heartbeat.
- One to three leads, wires that deliver electrical signals between the pulse generator and your heart.
- Electrodes at the ends of the leads, to help deliver the signals.
- A battery.
Types
In general, all pacemakers send out electrical pulses that stabilize your heart rhythm. But each type of pacemaker works differently.
Single-chamber pacemaker
A single-chamber pacemaker connects to one chamber of your heart, either your right ventricle (lower chamber) or your right atrium (upper chamber).
Dual-chamber pacemaker
This type of pacemaker has two leads that connect to both of the chambers — the ventricle and the atrium — on the right side of your heart. A dual-chamber pacemaker helps both of your heart’s chambers work better together.
Biventricular pacemaker
Also known as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), a biventricular pacemaker has three leads. Your cardiologist connects a lead to your right atrium, as well as a lead to your right and left ventricles. In general, this type of pacemaker is only necessary if you have severe arrhythmias caused by heart failure.
Common questions
If the electrical pathway described above is interrupted for any reason, changes in the heart rate and rhythm occur that make a pacemaker necessary.
Pacemakers are used to treat brady-arrythmias, slow heart rhythms that may occur as a result of disease in the heart’s conduction system (such as the SA node, AV node or His-Purkinje network). Pacemakers are also used to treat syncope (unexplained fainting spells), heart failure and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
A pacemaker can be implanted using the endocardial or epicardial approach.
The endocardial (transvenous) approach is the most common method. A local anesthetic (pain-relieving medication) is given to numb the area. An incision is made in the chest where the leads and pacemaker are inserted. The lead(s) is inserted through the incision and into a vein, then guided to the heart with the aid of the fluoroscopy machine. The lead tip attaches to the heart muscle, while the other end of the lead (attached to the pulse generator) is placed in a pocket created under the skin in the upper chest.
The epicardial approach is a less common method in adults, but more common in children. During this surgical procedure, general anesthesia is given to put you to sleep. The surgeon attaches the lead tip to the heart muscle, while the other end of the lead (attached to the pulse generator) is placed in a pocket created under the skin in the abdomen.
Although recovery with the epicardial approach is longer than that of the transvenous approach, minimally invasive techniques have enabled shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery times.
At CardioQ, Cardiac Pacemaker Specialist in Michigan (Beverly Hills) will determine which pacemaker implant method is best for you.
The pacemaker implant procedure may last from 2 to 5 hours.
A pacemaker implant is generally a very safe procedure. However, as with any invasive procedure, there are risks. Special precautions are taken to decrease your risks.
Please discuss your specific concerns about the risks and benefits of the procedure with your doctor.
