Cardiac Exercise Stress Test Specialist in Michigan
Cardiac Exercise Stress Test is an important diagnostic tool that is used to assess how well the heart is functioning under physical stress. At CardioQ, our team of highly trained and experienced Cardiac Exercise Stress Test Specialists in Michigan is dedicated to helping patients receive accurate and reliable test results that can help to guide their care and treatment.
Using state-of-the-art equipment and the latest techniques, our specialists work closely with patients to perform Cardiac Exercise Stress Tests that are tailored to their individual needs and medical history. Whether you are dealing with chest pain, shortness of breath, or other symptoms of heart disease, our team is here to provide you with the personalized care and attention you deserve.
At CardioQ, we are committed to helping our patients achieve optimal heart health through comprehensive testing, diagnosis, and treatment. Contact us today to schedule an appointment with one of our Cardiac Exercise Stress Test Specialists and take the first step toward a healthier heart.
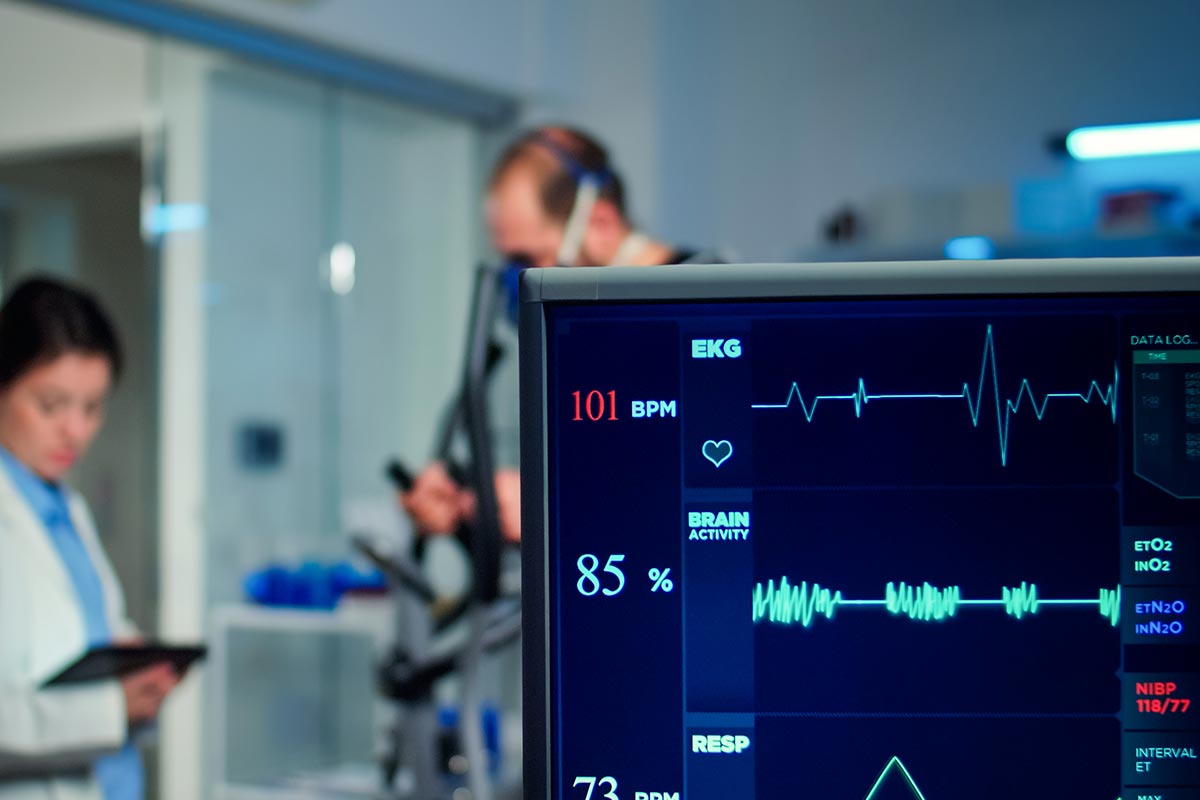
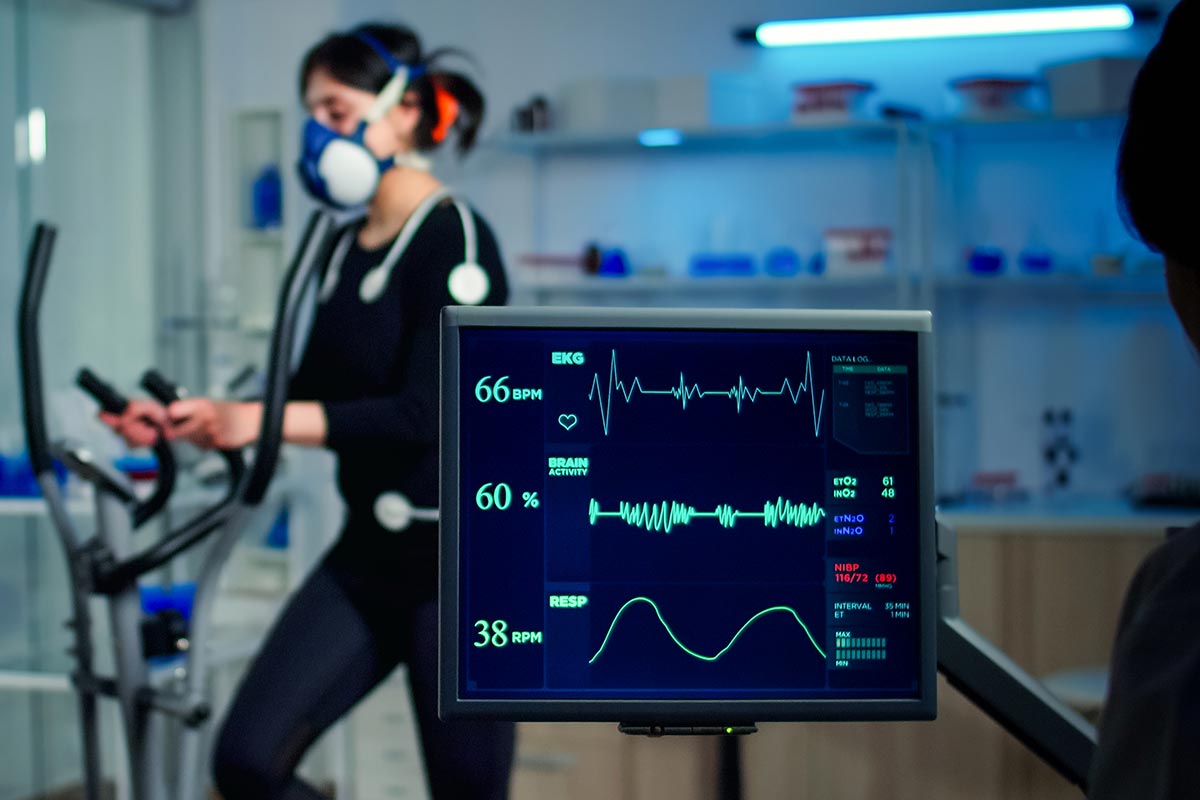

Stress Test or Cardiac Exercise Stress Test
A Cardiac Exercise Stress Test, also known as an exercise electrocardiogram (ECG), is a diagnostic test that is used to evaluate how well the heart functions during physical activity. During the test, the patient will be asked to walk on a treadmill or pedal a stationary bike while their heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG are monitored.
The goal of the test is to see how the heart responds to physical stress and to identify any abnormalities or irregularities in the heart’s rhythm or function that may not be apparent during rest. This can help to diagnose conditions such as coronary artery disease, heart valve problems, and arrhythmias.
The Cardiac Exercise Stress Test is a non-invasive and relatively low-risk procedure that typically takes between 30 minutes to an hour to complete. It is usually performed in a clinical setting by a trained specialist, such as a Cardiac Exercise Stress Test Specialist, and is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests to help provide a comprehensive picture of the patient’s heart health.
Overall, the Cardiac Exercise Stress Test is an important tool in the diagnosis and treatment of heart disease, and can help patients to better understand their heart health and take proactive steps to improve it.
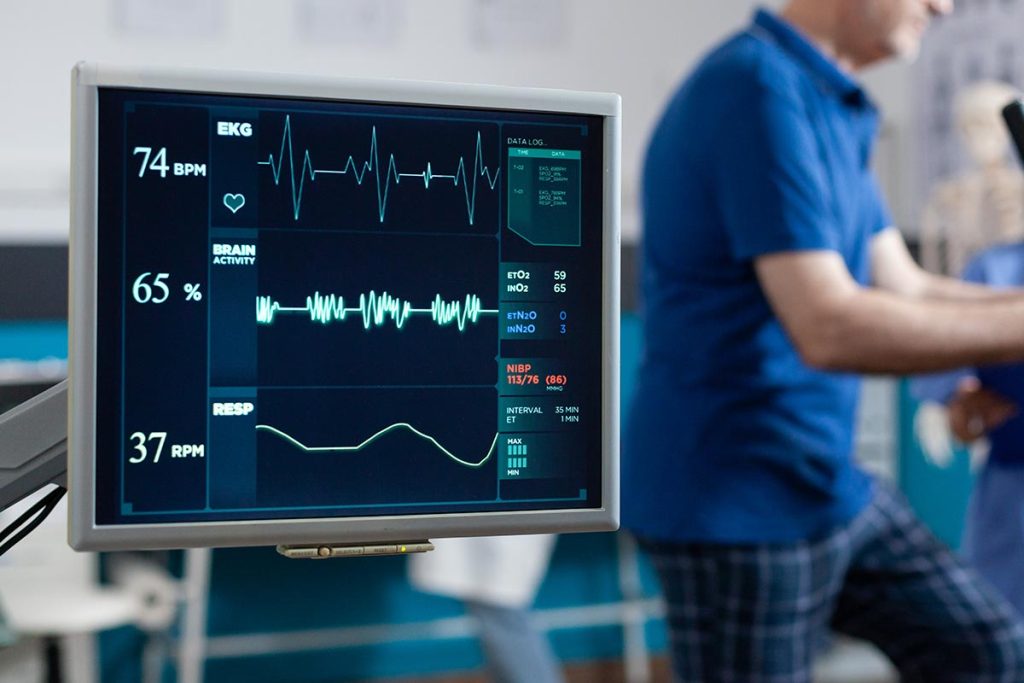
Time it Takes
The time taken by a Cardiac Exercise Stress Test can vary depending on a number of factors, including the specific protocol used for the test, the patient’s fitness level and medical history, and any complications that may arise during the test.
Typically, the test itself takes between 10 and 15 minutes, during which time the patient will be asked to walk on a treadmill or pedal a stationary bike while their heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG are monitored. However, the entire process, including preparation time, may take up to an hour or more.
Before the test, the patient may need to change into comfortable clothing and remove any jewelry or accessories that could interfere with the test. They may also need to avoid eating or drinking for a certain period of time before the test, as directed by their healthcare provider.
After the test, the patient will typically be monitored for a short period of time to ensure that their heart rate and blood pressure return to normal. The results of the test will then be reviewed by a Cardiac Exercise Stress Test Specialist or other healthcare provider, who will discuss the findings with the patient and recommend any necessary follow-up testing or treatment.
Getting the Results
After a Cardiac Exercise Stress Test, the results are typically interpreted and analyzed by a healthcare provider, such as a Cardiac Exercise Stress Test Specialist. The results will provide information on how well the heart is functioning during physical activity and can help to diagnose any underlying heart conditions or abnormalities.
The results of the Cardiac Exercise Stress Test are often recorded in a report that includes information such as the patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG readings before, during, and after the test. The report may also include any abnormal findings or recommendations for further testing or treatment.
Overall, the results of a Cardiac Exercise Stress Test are an important tool in assessing and managing heart health, and can provide valuable information for healthcare providers in determining the best course of care for their patients.
Common questions
There are several reasons why a healthcare provider may recommend a Cardiac Exercise Stress Test:
- To diagnose or evaluate coronary artery disease: Coronary artery disease is a condition where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked, which can lead to chest pain or a heart attack. A Cardiac Exercise Stress Test can help to diagnose or evaluate coronary artery disease by showing how well the heart functions during physical activity and identifying any abnormalities or irregularities in the heart’s rhythm or function that may indicate a problem.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of heart treatments: If a patient has been diagnosed with a heart condition, such as heart failure or arrhythmias, a Cardiac Exercise Stress Test can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and determine if any adjustments need to be made to the patient’s care plan.
- To assess overall heart health: A Cardiac Exercise Stress Test can also be used to assess a patient’s overall heart health and determine if they are at risk for developing heart disease or other conditions. This can be particularly important for patients with a family history of heart disease or other risk factors, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes.
There are several types of Cardiac Exercise Stress Tests:
- Treadmill Stress Test: This is the most common type of Cardiac Exercise Stress Test, where the patient walks or runs on a treadmill while their heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG are monitored.
- Dobutamine Stress Test: This test is used for patients who are unable to exercise on a treadmill, such as those with arthritis or respiratory problems. Instead of exercise, the patient is given a medication called dobutamine, which mimics the effects of exercise on the heart.
- Stress Echocardiogram: This test combines an exercise stress test with an echocardiogram, which uses ultrasound to create images of the heart. The images can help to detect any abnormalities in the heart’s function or structure.
- Nuclear Stress Test: This test uses a small amount of radioactive tracer that is injected into the patient’s bloodstream. As the tracer moves through the heart, a special camera is used to create images of the heart at rest and during exercise. The images can help to identify any areas of the heart that are not receiving enough blood flow.
The type of Cardiac Exercise Stress Test recommended by a healthcare provider will depend on the patient’s individual needs and medical history.
The exercise stress test involves exercising on a treadmill while you are closely monitored.
- Yes. However, DO NOT eat or drink anything except water for four hours before the test.
- Avoid all products that contain caffeine for 24 hours before the test. In general, caffeine is found in coffee, tea, colas and other soft drinks, most chocolate products, as caffeine will interfere with the results of the test. Also avoid decaffeinated or caffeine-free products for 24 hours before the test, as these product contain trace amounts of caffeine.
- DO NOT SMOKE ON THE DAY OF THE TEST, as nicotine will interfere with the results of your test.
A Cardiac Exercise Stress Test is typically performed by a healthcare provider, such as a cardiologist or a specialized technician, in a clinical setting such as a hospital or a clinic. Here is an overview of how the test is performed:
Preparation: Before the test, the patient may be asked to avoid eating, drinking, or smoking for a certain period of time. They may also be asked to stop taking certain medications or supplements. The patient will be asked to wear comfortable clothing and shoes suitable for exercise.
Baseline measurements: The healthcare provider will start by taking baseline measurements of the patient’s blood pressure, heart rate, and ECG while they are at rest.
Exercise: For a treadmill stress test, the patient will be asked to walk or run on a treadmill while the speed and incline gradually increase. For other types of stress tests, such as a dobutamine stress test or a nuclear stress test, the patient will be given a medication to increase their heart rate and mimic the effects of exercise. During the exercise, the healthcare provider will monitor the patient’s blood pressure, heart rate, and ECG.
Post-exercise measurements: After the exercise is complete, the patient will be asked to continue walking or resting while the healthcare provider monitors their blood pressure, heart rate, and ECG to evaluate their recovery.
Interpretation of results: The results of the Cardiac Exercise Stress Test will be interpreted by the healthcare provider, who will look for any abnormalities or irregularities in the patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, or ECG that may indicate a problem with the heart’s function or blood flow.
Overall, a Cardiac Exercise Stress Test is a safe and effective way to evaluate the function of the heart during physical activity, and can provide valuable information for healthcare providers in diagnosing and treating heart conditions.
The results of a Cardiac Exercise Stress Test can provide valuable information about the function of the heart and the presence of any heart-related issues. Here are some possible interpretations of Cardiac Exercise Stress Test results:
Normal results: A normal Cardiac Exercise Stress Test indicates that the heart is functioning well during physical activity, and there are no signs of blockages or other abnormalities.
Abnormal results: Abnormal results can indicate a variety of heart-related issues, such as poor blood flow to the heart, abnormal heart rhythms, or signs of heart disease or damage. Further testing may be needed to diagnose the specific issue.
Inconclusive results: In some cases, the results of a Cardiac Exercise Stress Test may be inconclusive, meaning that further testing or monitoring is needed to evaluate the heart’s function.
It’s important to remember that the interpretation of Cardiac Exercise Stress Test results is complex, and should be done by a healthcare provider with specialized training in interpreting these tests. They will take into account the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and other factors when evaluating the results, and will work with the patient to develop a plan for further testing or treatment if necessary.
